User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Doc for version ddk-3.4.7.7
YOLOv8n KSNN Demo - 2
YOLOv8n is an object detection model. It uses bounding boxes to precisely draw each object in image.
Inference results on VIM4.
Inference speed test: USB camera about 190ms per frame. MIPI camera about 140ms per frame.
Train the model
Download the YOLOv8 official code. ultralytics/ultralytics
$ git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
Refer README.md to create and train a YOLOv8n model. My version torch==1.10.1 and ultralytics==8.0.86.
Convert the model
Get the conversion tool
Get source khadas/vim4_npu_sdk.
$ git lfs install $ git lfs clone https://github.com/khadas/vim4_npu_sdk $ cd vim4_npu_sdk $ ls adla-toolkit-binary adla-toolkit-binary-3.1.7.4 convert-in-docker.sh Dockerfile docs README.md
Please use convert tool version branch npu-ddk-3.4.7.7 or higher.
Convert
After training the model, modify ultralytics/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py as follows.
- head.py
diff --git a/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py b/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py index 0b02eb3..0a6e43a 100644 --- a/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py +++ b/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py @@ -42,6 +42,9 @@ class Detect(nn.Module): def forward(self, x): """Concatenates and returns predicted bounding boxes and class probabilities.""" + if torch.onnx.is_in_onnx_export(): + return self.forward_export(x) + shape = x[0].shape # BCHW for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i])), 1) @@ -80,6 +83,15 @@ class Detect(nn.Module): a[-1].bias.data[:] = 1.0 # box b[-1].bias.data[:m.nc] = math.log(5 / m.nc / (640 / s) ** 2) # cls (.01 objects, 80 classes, 640 img) + def forward_export(self, x): + results = [] + for i in range(self.nl): + dfl = self.cv2[i](x[i]).contiguous() + cls = self.cv3[i](x[i]).contiguous() + results.append(torch.cat([cls, dfl], 1)) + return tuple(results) +
If you pip-installed ultralytics package, you should modify in package.
Create a python file written as follows to export ONNX model.
- export.py
from ultralytics import YOLO model = YOLO("./runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt") results = model.export(format="onnx")
$ python export.py
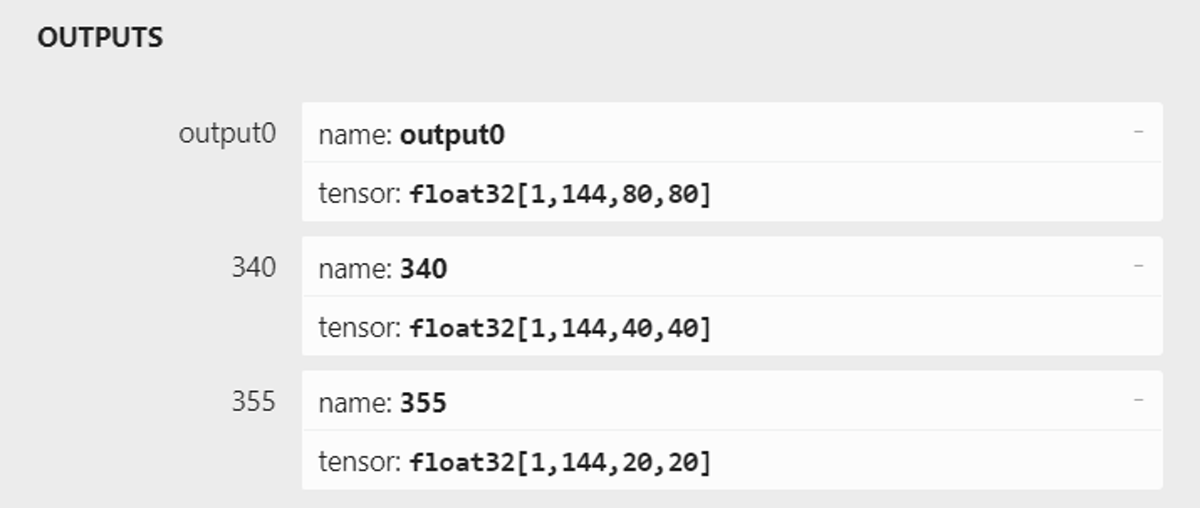
Use Netron to check your model output like this. If not, please check your head.py.
Pull yolov8n.onnx model into vim4_npu_sdk/adla-toolkit-binary-3.1.7.4/python and then run convert-in-docker.sh
$ ./convert-in-docker.sh ksnn
If your yolov8n model parameters are different from ours, you can change parameters in ksnn_args.txt.
Run inference on the NPU by KSNN
Install KSNN
Download KSNN library and demo code. khadas/ksnn-vim4
$ git clone https://github.com/khadas/ksnn-vim4.git
If you use Ubuntu 24.04, demo must run in python virtual environment.
Create and start python virtual environment.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install python3-venv $ python3 -m venv myenv $ source myenv/bin/activate
Install KSNN package.
$ cd ksnn-vim4/ksnn $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install python3-pip $ pip3 install ksnn_vim4-1.4.1-py3-none-any.whl
Please use KSNN VIM4 version v1.4.1 or higher.
Put yolov8n.nb and libnn_yolov8n.so into ksnn/examples/yolov8n/models/VIM4 and ksnn/examples/yolov8n/libs
If your model's classes is not 80, please remember to modify the parameter, LISTSIZE.
LISTSIZE = classes number + 64
Picture input demo
$ cd ksnn/examples/yolov8n $ export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=xcb $ python3 yolov8n-picture.py --model ./models/VIM4/yolov8n_int8.adla --library ./libs/libnn_yolov8n.so --picture ./data/horses.jpg --level 0
Camera input demo
$ cd ksnn/examples/yolov8n $ export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=xcb # USB Camera $ python3 yolov8n-cap.py --model ./models/VIM4/yolov8n_int8.adla --library ./libs/libnn_yolov8n.so --type usb --device 0 # MIPI Camera $ python3 yolov8n-cap.py --model ./models/VIM4/yolov8n_int8.adla --library ./libs/libnn_yolov8n.so --type mipi --device 63
0 is the camera device index.
If you want to use MIPI Camera, you should remove OpenCV in python lib and then us apt install OpenCV.
$ pip3 uninstall opencv-python $ sudo apt install python3-opencv
If you use virtual environment, you need to download the opencv source code and compile the GSTREAMER function manually. (If you do not know how to compile, you can ask help in KHADAS FORUM).